Transportation (EVs & Emerging Mobility)
Reasons Why Electric Vehicles Will Inevitably Overtake Internal Combustion

The Economics of Total Cost Ownership
Efficiency
Electrical vehicles energy cost is 2 to 3 ¢/km (at 15 ¢/kWh), compared to a typical 6 cylinder gasoline vehicle at 10 to 12 ¢/km (at $1.50/L). Regenerative braking recaptures energy lost during deceleration, improving efficiency and extending EV range.
Maintenance
Electric vehicles (EVs) have a lower total cost of ownership. This is because EVs have fewer moving parts, use regenerative braking, and have lower wear and tear on brake pads and callipers.
Convenience
EVs offer home charging convenience, quieter operation, and instant torque, while ICE vehicles still excel in quick refueling. However, the gap is narrowing with the rapid expansion of fast-charging infrastructure.
Sustainable Energy Source
EVs can be charged using renewable energy sources like solar, geothermal or wind power. Future EVs will integrate solar panels for passive charging and utilize wireless charging embedded in roads, enabling continuous energy replenishment while driving.
Environmental Benefits
EVs significantly reduce carbon emissions by eliminating tailpipe pollution, helping combat climate change and improve air quality. As battery and motor technology evolves, innovations in alternative materials will reduce dependency on critical minerals, making EVs even more environmentally friendly.
Human Health
EV drivers enjoy a quieter, smoother ride, reducing stress and fatigue, while the lack of emissions lowers exposure to harmful pollutants, improving respiratory health—especially in urban areas.
EVs vs. ICE: The Superior Energy Efficiency of Electric Vehicles
Electric vehicles (EVs) are significantly more energy efficient than internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles, with EVs converting a much larger percentage of their energy source into motion, making them considerably more efficient overall; typically, an EV can achieve over 80% efficiency compared to an ICE vehicle's 20-30% efficiency.
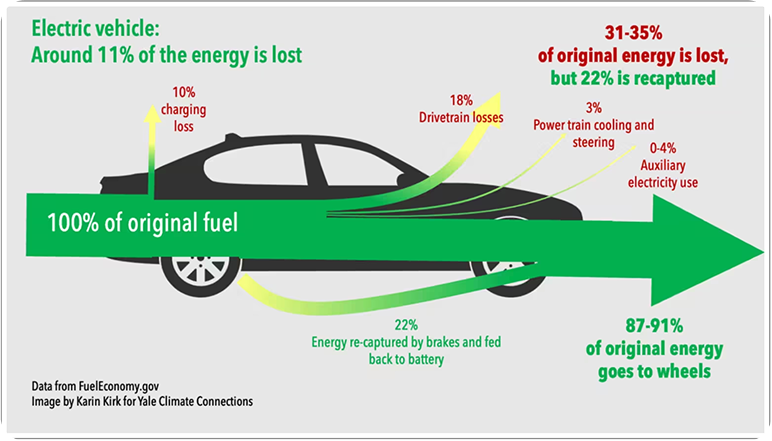
Electric vehicles (EVs) utilize energy far more efficiently, with 87-91% of their original energy reaching the wheels.
Regenerative braking helps recapture up to 22% of lost energy, improving overall efficiency.
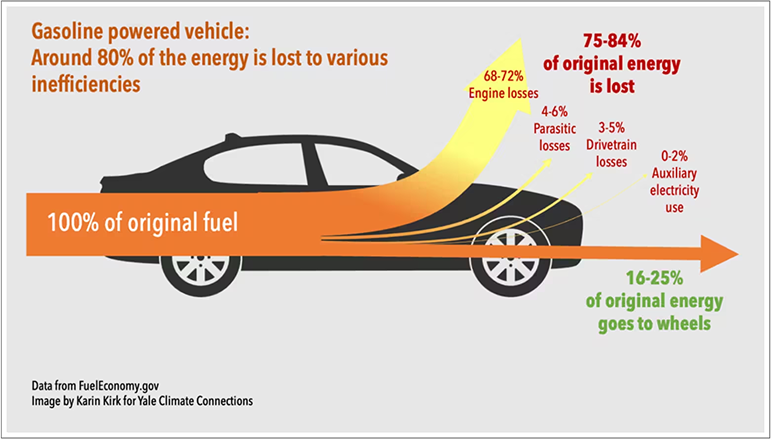
Internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles lose 75-84% of their original energy to inefficiencies, including engine losses, drivetrain losses, and parasitic losses, with only 16-25% of energy reaching the wheels
Global EV Market Trends: Growth, Challenges, and Emerging Opportunities
Electric vehicle markets around the world are not all travelling in the same direction or at the same speed in 2024. Sales of EVs continue to rise globally, but some markets are experiencing a significant slowdown and many automakers have pushed back their EV targets.
Progress varies by segment, with electric commercial vehicles set for another blistering year and segments like buses and two- and three-wheelers already reaching very high levels of electrification.
EV Adoption Expands Beyond Wealthy Markets
Electric vehicles are no longer only a wealthy country phenomenon. Developing economies like Thailand, India, Turkey, Brazil and others are all experiencing record sales as more low-cost electric models are targeted at local buyers. Chinese automakers are expanding quickly abroad as they look for new markets for their EVs.
Advancements in Battery Technology and Cost Reductions
The underlying technology for electrification continues to improve. Several next-generation battery technologies are reaching commercialization in the next few years and prices have fallen by 90% over the past decade. This trend looks set to continue, with early indications that prices are dropping sharply in 2024 due to lower raw-material prices, manufacturing advances, and overcapacity. This is good news for automakers and EV buyers but marks a challenging time ahead for new entrants to the battery industry.
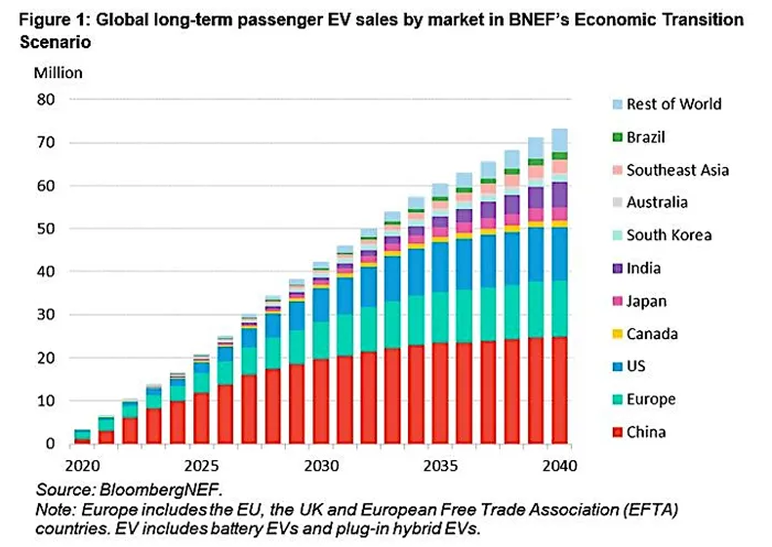
Projected Global EV Sales Growth: Long-term passenger EV sales are expected to rise significantly across all major markets, with China and Europe leading the transition through 2040.