Electrical Energy Storage Solutions
Transitioning from Petro-States to Electro-States by creating the next-generation intelligent electrical grid.

Electrical Energy is a fundamental necessity for carrying out day-to-day activities across private, commercial, industrial, and numerous different verticals. Energy independence is one of the most important challenges countries are currently faced with, we are witnessing a massive push at a global scale towards various renewable energy solutions.
A traditional utility grid primarily delivers electricity directly from power plants to consumers, while battery storage acts as a buffer, storing excess electricity during low demand periods and releasing it back to the grid when demand spikes, offering greater flexibility and grid stability by managing fluctuations in power generation and consumption; essentially, a traditional grid is a constant flow of electricity, whereas battery storage allows for dynamic adjustments based on real-time needs.
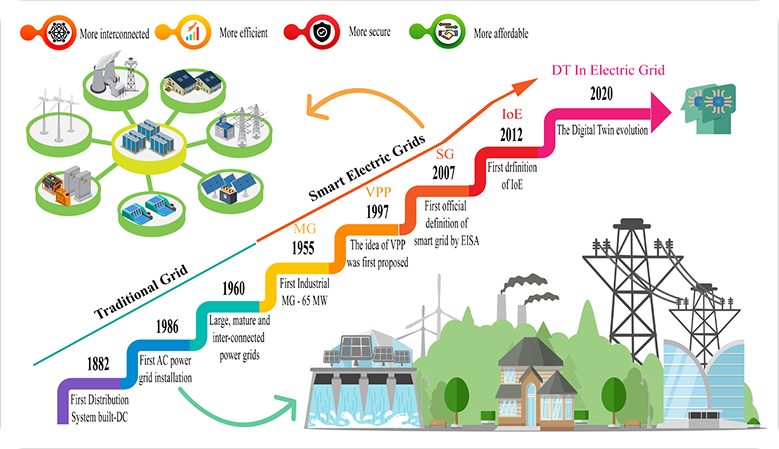
The Evolution of Power Grids: From Traditional Infrastructure to Smart, Efficient, and Interconnected Energy Systems.
Battery Storage Systems: Enhancing Energy Security, Savings, and Sustainability
Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) offer significant advantages for industrial, commercial, and residential energy users. From backup power during outages to cost savings and grid stability, BESS plays a critical role in energy independence and sustainability. As energy markets evolve, the adoption of BESS continues to grow, providing reliable, efficient, and resilient power solutions.
Key Benefits of Battery Storage Systems
Backup Power
BESS can provide power during outages, which can help critical infrastructure like hospitals and data centers continue to operate. BESS can also help businesses avoid costly disruptions and lost productivity.
Energy Independence
BESS can provide a source of power that's available even when the sun isn't shining. This can help consumers shield themselves from volatile energy prices.
Cost Savings
BESS can help consumers save money by charging during off-peak times when energy prices are lower. This practice is known as load shifting or peak shaving.
Grid Stabilization
BESS can help relieve stress on utility companies by stretching the usefulness of energy to later periods in the day. This can contribute to the health of the larger power grid.
Reduced Carbon Footprint
BESS can help reduce a household's carbon footprint. For example, a household that installed solar panels and a BESS could reduce CO2 emissions by around 14 tons over the system's lifespan.
Energy Resilience
BESS can provide fast response backup power in the event of a mains failure.
Safety and Fire Prevention
BESS can provide mission-critical backup power during extreme weather events so utilities can shut down their electrical networks to avoid starting forest fires during the extreme weather events.
The Rapid Growth and Cost Advantage of Battery Storage
In recent years the battery storage industry has tripled. The global battery energy storage market size was valued at USD 25 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow to USD 114.05 billion by 2032, exhibiting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 20.88% from 2024 to 2032.
According to recent studies, battery storage is generally considered more cost-effective than building new gas peaker plants, with some analyses showing battery storage being 30% cheaper per unit of capacity when used for peak demand management. This is largely due to the significant decline in battery costs in recent years, making them a more attractive option for replacing older gas peaker plants.
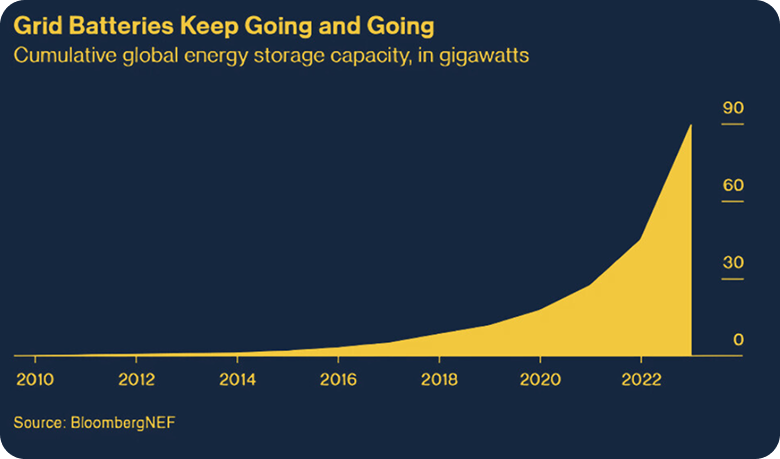
Global energy storage capacity is experiencing exponential growth, driven by advancements in battery technology and increasing demand for grid stability.
Key Considerations for Utilities: Gas Peaker Plants vs. Battery Storage Investments
Lower capital costs
Battery storage technology has seen rapid cost reductions due to falling battery prices, making the initial investment for a battery system considerably lower than a gas peaker plant.
Operational costs
While gas peaker plants only run during peak demand periods, they still incur significant operational costs even when not actively generating power, whereas battery storage can be more efficient in managing peak demand with lower running costs.
Environmental impact
Battery storage offers a significant environmental advantage by eliminating greenhouse gas emissions associated with gas combustion.
The Global Rise of Battery Storage: Key Growth Drivers
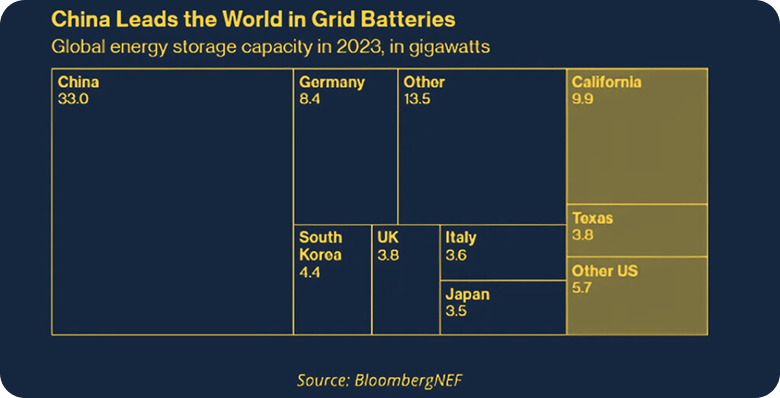
Global battery storage capacity in 2023, highlighting China as the leading market, followed by the U.S. and Germany.
Key Factors Driving the Growth of Battery Storage
Renewable Energy
Battery storage allows excess energy from renewable sources like wind and solar to be stored for use when demand is higher.
Electricity Demand
The power and automotive sectors are both driving demand for battery storage.
Grid Stability
Battery storage systems can absorb and release power quickly, helping to balance supply, and demand, and maintain a steady frequency.
Backup Power
Battery storage systems can provide power during outages, which is especially important for businesses that need a continuous power supply.
Cost
The cost of lithium iron phosphate (LFP) batteries has been declining due to technological advancements, economies of scale, and increased manufacturing efficiency.
Government Support
Policies like tax incentives and procurement mandates can encourage the use of battery storage.