Autonomous Mobility
The Global Need for Autonomous Vehicles and Trucks
Autonomous driving is essential for its potential to enhance road safety by minimizing human error, reduce traffic congestion through optimized route planning and vehicle coordination, expand mobility access for individuals unable to drive, and support environmental sustainability by improving fuel efficiency and lowering emissions.
Strategic Advantages of Adopting Autonomous Vehicles:
Reduced Traffic Accidents
The majority of car accidents are caused by human error, which autonomous vehicles can largely eliminate by consistently following traffic rules and reacting faster than humans.
Improved Traffic Flow
Self-driving cars can communicate with each other and coordinate movements to optimize traffic flow, reducing congestion and travel time.
Enhanced Accessibility
Autonomous vehicles can provide transportation options for people who are unable to drive themselves due to age, disability, or medical conditions.
Environmental Benefits
By optimizing routes, maintaining smoother acceleration and braking, and potentially enabling vehicle platooning, autonomous cars can contribute to reduced fuel consumption and emissions.
Increased Productivity
People can utilize commuting time productively while an autonomous vehicle drives, enhancing work efficiency.
The Future of Self-Driving Vehicles: Market Growth and Adoption Trends
The self-driving vehicle market is expected to grow significantly in the coming decades. This growth is driven by advancements in technology, government support, and consumer demand.
As of today, the strongest candidates to become fully automated are passenger cars, including private cars and shared autonomous vehicles, also known as robo-taxis or shuttles; the second segment is autonomous truck platooning. It is forecast that by 2040, there will be over 33 million driverless vehicles on the road.
Understanding the Levels of Autonomous Driving
Autonomous vehicle technology is evolving rapidly, with automation levels ranging from basic driver assistance to fully self-driving capabilities. The SAE J3016™ framework categorizes automation into six levels, from Level 0 (no automation) to Level 5 (full autonomy under all conditions).
• Levels 0-2: Require constant human supervision, with features like adaptive cruise control and lane centering assisting the driver.
• Levels 3-5: Mark the transition to automated driving, where the system takes control under specific conditions, with Level 5 representing full autonomy in all scenarios.
Currently, Level 2+ automation is widely available in consumer vehicles, while Level 3 and Level 4 systems are being tested for deployment in controlled environments, such as urban robotaxis and highway driving.
Regulatory frameworks, infrastructure, and AI advancements will determine how quickly higher-level automation becomes mainstream. As automakers and tech firms push forward, the goal remains the same: improving safety, reducing congestion, and reshaping mobility as we know it.
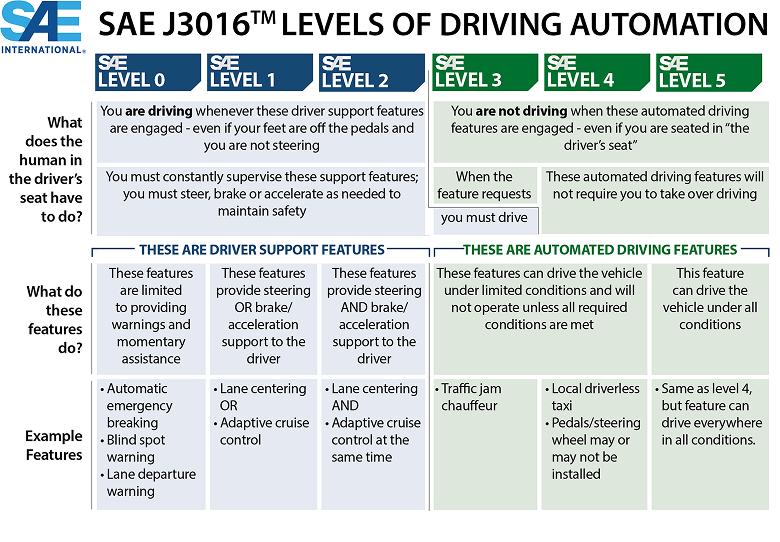
SAE J3016™ defines vehicle automation levels from driver assistance (Level 0-2) to full autonomy (Level 5).
The Autonomous Vehicle Market: Growth Projections, Key Drivers, and Industry Impact
Market Size
• Fortune Business Insights projects that the autonomous vehicle market will grow from $1,921.1 billion in 2023 to $13,632.4 billion by 2030.
• Skyquest projects that the autonomous vehicle market will grow from $71.78 billion in 2024 to $933.22 billion by 2032.
Key Factors
• Technology: Sensor technologies like LiDAR and radar, vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication, cloud computing, and AI-based decision-making
• Government support: Favorable policies and initiatives in emerging markets and intelligent cities
• Consumer demand: For safer and more convenient mobility solutions
• Business models: New business-to-business insurance models for autonomous travel
Other Considerations
• High costs of development and regulatory uncertainties
• The emergence of robo-taxis and mobility-as-a-service (MaaS) solutions
• The impact on other industries, such as roadside assistance and repairs